Key U.S. Regulatory Agencies
Importing or exporting chemical, biological, or radioactive materials often requires specialized permits to ensure timely and lawful customs clearance. These materials are regulated by multiple U.S. government agencies, each with its own set of requirements.
- Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) - Department of Commerce
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- Department of Transportation (DOT)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS)
- USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) Organisms and Vectors Permits
- USDA Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) Biotechnology Permits
- United States Postal Service (USPS), Special Requirements for Shipping Internationally
Each agency plays a role in ensuring the safe and compliant transport of sensitive materials.
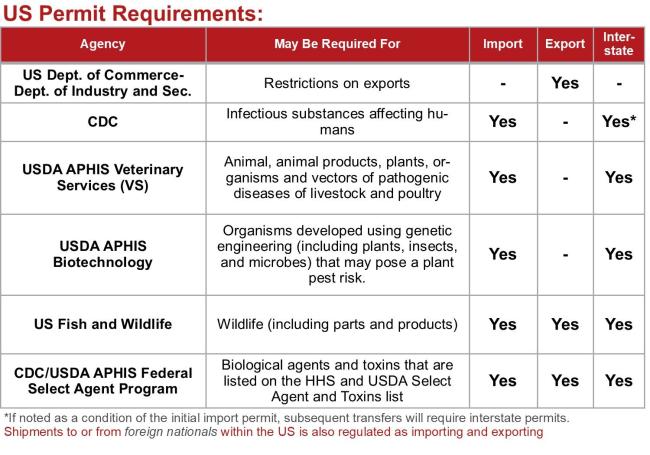
Permit Requirements Across U.S. Regulatory Agencies
Permit Decision Tools
To help determine if a permit is required, several agencies provide online resources:
BIS - Bureau of Industry and Security
Access key tools from the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) to assist with export classification and compliance. These interactive resources include the Commerce Control List (CCL), Country Chart, and Country Groups, which are used to determine licensing requirements under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR).
CDC – Import Permit Program (IPP)
USDA/APHIS – U.S. Department of Agriculture – Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service– Organisms and Vectors
Helpful sections include:
- “What’s New?”
- “VS-regulated livestock and poultry pathogens”
- “Guidelines for No Import Permit Required”
- “Guideline 1125: No Interstate Transport Permit Required”
- Veterinary Services Permitting Assistant
USFWS - U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
Secondary Transfer Approvals
In some cases, materials that have already been imported cannot be transferred to another recipient without additional approval.
For example, the CDC requires further authorization for materials suspected or confirmed to contain the following infectious biological agents:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Coronaviruses (SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV)
- Influenza viruses (H2N2, H6N1, low pathogenic avian H7N9)
- Viral hemorrhagic fevers (e.g., Tick-borne encephalitis viruses, Old World hantaviruses causing HFRS)
- Mpox (clade II, formerly Monkeypox – West African clade)
- Poliovirus (serotypes 1, 2, 3)
